Aristo
Building the next generation of systems that can systematically reason, explain, and continually improve over time

- Systematic reasoning and explanation
- Teachable reasoning systems
- Continual learning with memory-based architectures
- Knowledge and belief
- Universal mathematical reasoning
Recent Updates
Towards Teachable Reasoning Systems
April 27, 2022This paper describes our work towards Teachable Reasoning Systems. First, EntailmentWriter searches for a chain of reasoning from facts it believes…
Memory-assisted prompt editing to improve GPT-3 after deployment
April 20, 2022Large LMs such as GPT-3 are powerful, but can commit mistakes that are obvious to humans. Memory-assisted prompt editing allows users to give…

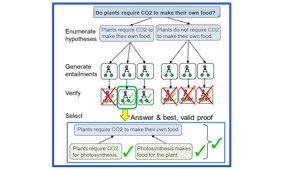
DREAM: Improving Situational QA by First Elaborating the Situation
March 1, 2022When people answer questions about a specific situation, e.g., "I cheated on my mid-term exam last week. Was that wrong?", cognitive science suggests…
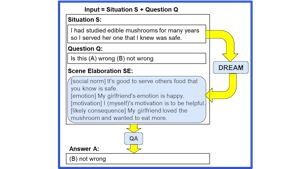
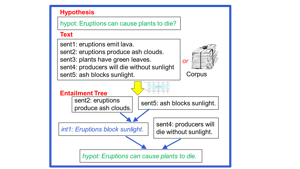
Explaining Answers with Entailment Trees
November 1, 2021EntailmentBank is a unique dataset of multi-step entailment trees. Each tree shows how known facts combine to entail the answer to a question. From…
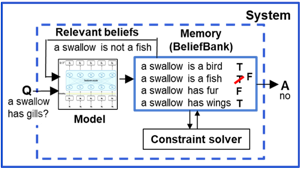
BeliefBank: Adding Memory to a Pre-Trained Language Model for a Systematic Notion of Belief
November 1, 2021Although pretrained language models (PTLMs) contain significant amounts of world knowledge, they can still produce inconsistent answers to questions…
Research Areas
Teachable Reasoning Systems
By interacting with and giving feedback on a system’s reasoning, a user can teach the system so it continually improves over time – without model retraining.
Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning and Explanation
Solving problems by generating consistent, faithful chains of reasoning using neural components.
Modular Models
By learning to chain together existing models, complex problems can be solved, beyond the capabilities of the individual components.
Universal Mathematical Reasoners
Creating models with built-in mathematical reasoning skills, that can be rapidly fine-tuned for a wide variety of mathematical tasks.
Macaw is a high-performance question-answering (QA) model capable of outperforming other popular current language models, all while being an order of magnitude smaller. This demo allows you to explore Macaw's answers and compare them to those of the popular GPT-3 language model on a benchmark set of questions.
Try the demo

Macaw is a high-performance question-answering (QA) model capable of outperforming other popular current language models, all while being an order of magnitude smaller. This demo allows you to explore Macaw's answers and compare them to those of the popular GPT-3 language model on a benchmark set of questions.
Try the demo
Like RuleTaker, ProofWriter determines whether statements are True or False based on rules given in natural language - but also generates the proof of its answers.
Try the demo
Like RuleTaker, ProofWriter determines whether statements are True or False based on rules given in natural language - but also generates the proof of its answers.
Try the demoRecent Papers
ADaPT: As-Needed Decomposition and Planning with Language Models
Archiki Prasad, Alexander Koller, Mareike Hartmann, Peter Clark, Ashish Sabharwal, Mohit Bansal, Tushar KhotNAACL Findings • 2024 Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being used for interactive decision-making tasks requiring planning and adapting to the environment. Recent works employ LLMs-as-agents in broadly two ways: iteratively determining the next action (iterative…Leveraging Code to Improve In-context Learning for Semantic Parsing
Ben Bogin, Shivanshu Gupta, Peter Clark, Ashish SabharwalNAACL • 2024 In-context learning (ICL) is an appealing approach for semantic parsing due to its few-shot nature and improved generalization. However, learning to parse to rare domain-specific languages (DSLs) from just a few demonstrations is challenging, limiting the…QualEval: Qualitative Evaluation for Model Improvement
Vishvak Murahari, Ameet Deshpande, Peter Clark, Tanmay Rajpurohit, Ashish Sabharwal, Karthik Narasimhan, Ashwin KalyanNAACL • 2024 Quantitative evaluation metrics have traditionally been pivotal in gauging the advancements of artificial intelligence systems, including large language models (LLMs). However, these metrics have inherent limitations. Given the intricate nature of real-world…SelfGoal: Your Language Agents Already Know How to Achieve High-level Goals
Ruihan Yang, Jiangjie Chen, Yikai Zhang, Siyu Yuan, Aili Chen, Kyle Richardson, Yanghua Xiao, Deqing Yangtechnical report • 2024 Language agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly valuable as decision-making tools in domains such as gaming and programming. However, these agents often face challenges in achieving high-level goals without detailed instructions and…Digital Socrates: Evaluating LLMs through explanation critiques
Yuling Gu, Oyvind Tafjord, Peter ClarkACL • 2024 While LLMs can provide reasoned explanations along with their answers, the nature and quality of those explanations are still poorly understood. In response, our goal is to define a detailed way of characterizing the explanation capabilities of modern models…
Recent Datasets
IfQA Counterfactual Reasoning Benchmark
3,800 open-domain questions designed to assess counterfactual reasoning abilities of NLP models
Counterfactual reasoning benchmark introduced in the EMNLP-2023 paper titled "IfQA: A Dataset for Open-domain Question Answering under Counterfactual Presuppositions".
Digital Socrates
DS Critique Bank contains annotated critiques of answers and explanations from "student" models.
DS Critique Bank (DSCB) is a dataset of multiple-choice questions with associated answers and explanations provided by "student models", along with "critiques" of the explanations provided by "critique models". Many of the instances have human annotations.
ParRoT (Parts and Relations of Things)
11,720 “X relation Y?” True/False questions on parts of everyday things and relational information about these parts
This is the dataset in "Do language models have coherent mental models of everyday things?", ACL 2023.
Belief and Reasoning Dataset
BaRDA: A Belief and REasoning Dataset that Separates Factual Accuracy and Reasoning Ability
BaRDa is a new belief and reasoning dataset for evaluating the factual correctness ("truth") and reasoning accuracy ("rationality", or "honesty") of new language models. It was created in collaboration with, and with the support of, the Open Philanthropy organization.
Recent Press
How Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Helps Neural Networks Compute
March 21, 2024
Persona-driven ChatGPT yields toxic, racist output
April 19, 2023
Changing ChatGPTs Persona Might Make It Malicious
April 17, 2023
This AI Paper Shows How ChatGPT’s Toxicity Can Increase Up To Six-Fold When Assigned A Persona
April 14, 2023
'They’re All So Dirty and Smelly:' Study Unlocks ChatGPT's Inner Racist
April 13, 2023
New study reveals ChatGPT's inherent toxicity when assigned different personas
April 13, 2023
Researchers discover a way to make ChatGPT consistently toxic
April 12, 2023
ChatGPT can turn toxic just by changing its assigned persona, researchers say
April 12, 2023
Team
 Chris Callison-BurchResearch
Chris Callison-BurchResearch Peter ClarkResearch
Peter ClarkResearch Ben BoginYoung Investigator
Ben BoginYoung Investigator Bhavana DalviResearch
Bhavana DalviResearchYuling GuPredoctoral Young Investigator
 Shashank GuptaResearch
Shashank GuptaResearch Tushar KhotResearch
Tushar KhotResearch Bodhisattwa Prasad MajumderResearch
Bodhisattwa Prasad MajumderResearch Kyle RichardsonResearch
Kyle RichardsonResearch Ashish SabharwalResearch
Ashish SabharwalResearch Oyvind TafjordResearch
Oyvind TafjordResearch Niket TandonResearch
Niket TandonResearch Sarah WiegreffeYoung Investigator
Sarah WiegreffeYoung Investigator











